Every morning this week, I’m running a series of guests posts about different printing methods – so if you’ve ever wondered why certain printing methods are best for certain kinds of designs (or cost more than others), this is for you! You can read the previous installments covering digital printing, engraving, screen printing, letterpress printing with antique type, and foil stamping all right here. Today, the talented team at Egg Press is here to talk about the technique known as die-cutting, which they use to produce unique shapes, edges, and message windows in greeting cards and other stationery design elements.
What is Die Cutting?
Die-cutting is a process used in many different industries to cut a thin flat material (in our case, paper) into a specific shape using a steel cutting die. It can be used to punch out a decorative shape or pattern to incorporate within a larger piece, or it can be used to create the main shape of an object by cutting the entire sheet of paper in an distinct/designed way. More simply put: for us it’s way of making a hole in paper in a desired shape using the same presses that we use for letterpress printing.
Like letterpress, a die-cut element draws attention to the 3D nature of paper and the character of the material itself. We mostly use die-cutting as a feature – taking an industrial process and turning it into a design element. As a letterpress print shop, here are some common ways we use die-cutting:
- to create die-cut windows for messages on greeting cards
- to create a unique shaped greeting card (examples include heart die-cuts, scallops, mini-paper sculptures)
- as a design element in one of our new wedding suites
- to create die-cut coasters, hang tags, and rounded corners on business cards for clients
- to make the boxes in which our cards are packaged
The Printing Process
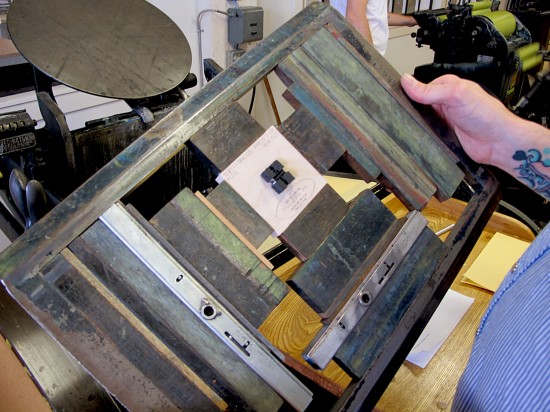
The process of die-cutting is easy for us as letterpress printers, as the set-up is similar to letterpress printing. Instead of a type-high printing plate we use a type high wood mounted steel cutting die. The shape of the cutting die is often something we’ve designed and ordered from our local die-makers. Instead of tympan paper and packing (used to control the impression when printing), we use a sheet of metal on the press bed giving the die a hard surface to cut against.
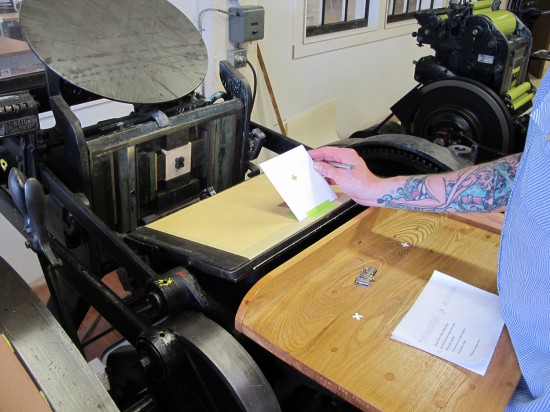
The first few steps are essentially the same as letterpress printing, although since we’re not using ink we’re always sure to remove the rollers from the press before we start. We don’t want the dies to damage our rubber rollers!
Next, we attach metal plate/backing onto the press bed by locking the die into the chase and inserting the chase into the press. Then we’re ready to turn on the press and make a cut.
Pop out the cut shape (paper is still taped to press bed). Slide your mock-up proof underneath – align your mock up with the cut sample – hold in place. Make any necessary adjustments, start cutting, and enjoy the confetti!
Tips + Advice
Though die-cutting can produce unique results, it’s not for every print job. This is why it’s not very commonly used, and why it can be so distinctive. A die-cut can add a decorative element or a functional component to a design. For stationery or invitations, creating a die-cut silhouette for your suite may add interest and a vintage feel. Using a small punch-out within the invitation as a motif can be a nice touch (in this case, a modern feel). A functional die-cut might be something like a half-moon thumb hole on an open ended envelope, or a notch system in a folded piece. There are many possibilities for die-cutting, but the medium has limitations.
Complicated shapes or patterns may not work (ask your printer or die-maker). There is a minimum size for die-cut elements. The maximum size of the die-cut will depend on the capability of the press you are using.
Paper can affect the outcome – this is something to consider when choosing your paper or choosing to use a die-cut element. In our experience, thinner paper has less resistance and seems to cut more cleanly while thicker stock can yield mushy edges. Cotton paper can leave a ragged edge. Finally, when mailing something with a die-cut element it’s a good policy to mail it in an envelope for protection. It might not be a good choice for a postcard mailer or rsvp card.
Thanks guys! Check out awesome stationery from Egg Press right here!
Photo Credits: Egg Press
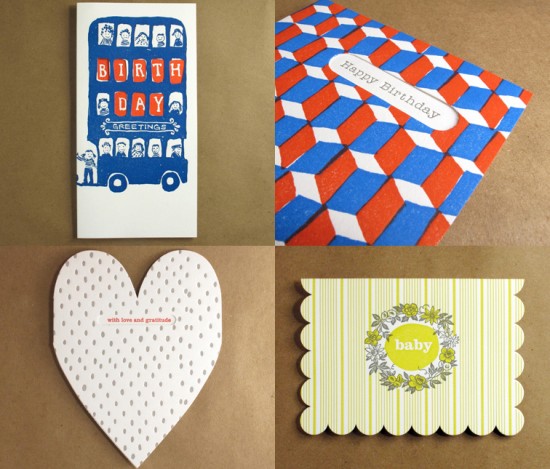







Egg Press die cut cards are *always* among my favorites to send. They are just TOO cute!
Thanks for this! Could you please also make a post or further explanation about the process of die-cut making, and how these things work? Thanks!
die cutting is hella lit